

- #Skype for business share audio from desktop code#
- #Skype for business share audio from desktop series#
In addition to the work required, as more and more applications move to SaaS available across the Internet, QoS is lost as the traffic leaves the corporate network and moves across the Internet which restricts QoS from being available from end-to-end.Ĭontrol the traffic through the applicationįor most of the application engineers out there, this is the “preferred method”. While flexible and powerful, this method requires engineers to know all the various types of traffic on the network and to classify it accordingly (and ensure it is classified across all devices), which can be an arduous task and result in traffic being incorrectly classified.
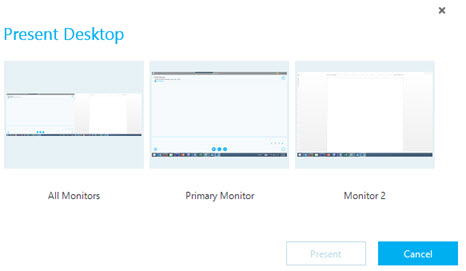
In either case above, network engineers can control, on a per-hop basis, how each classification of traffic is treated along the entire network path. This is not a common QoS model still in deployment.
#Skype for business share audio from desktop code#
Differentiated Services Code Point (DSCP) – This is a Network Layer classification method whereby a 6-bit DSCP value is included in the 8-bit Differentiated Services field within the IP headers of traffic.Class of Service (CoS) – This is a Data Link Layer classification method whereby a 3-bit CoS field is included in Ethernet headers in a 802.1Q VLAN.Differentiated Services – This is a QoS designation split into two layers of the OSI stack.This is most generally referred to as Quality of Service (QoS). Like controlling traffic on highways via “normal lanes” and “HOV lanes”, network traffic is separated, classified and handled in a manner that is configured by the network engineers to give preferential treatment (and bandwidth) to high priority traffic while giving normal treatment to non-priority traffic. Both methods are not mutually exclusive and can be used in concert with one another, but it is largely up to network engineers and the application engineers to work together to find the best solution for your environment.įor most of the network engineers out there, this is the “preferred method”. Speaking broadly, there are typically two methods of controlling any sort of application bandwidth across enterprise networks.
#Skype for business share audio from desktop series#
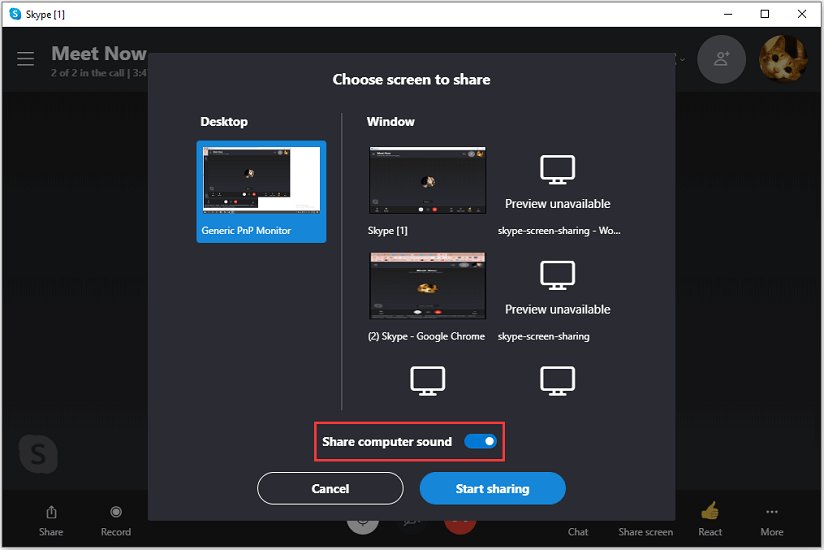
Armed with that information, the next logical progression of this blog series continues the focus on application sharing and discusses the available methods within Skype4B to manage and control the bandwidth requirements for application sharing. In a previous blog post I talked about how administrators and architects should place more emphasis on planning for application sharing bandwidth in their Skype4B deployments.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
